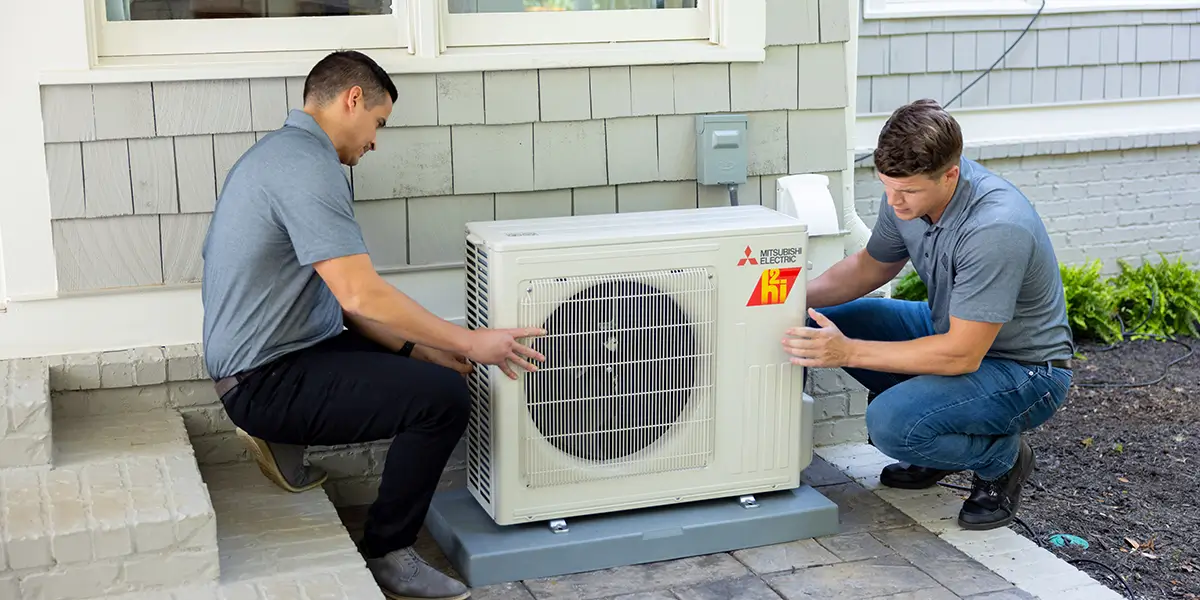
Are Mini-Splits used for heating or for cooling? The answer is both! While many people are…
Continue readingNavigating The Rebate Maze
Local Utilities Offer Generous Rebates to Mini-Split Buyers. Why? To promote energy…
Continue readingHow Does Ductless Heating & Cooling Work?
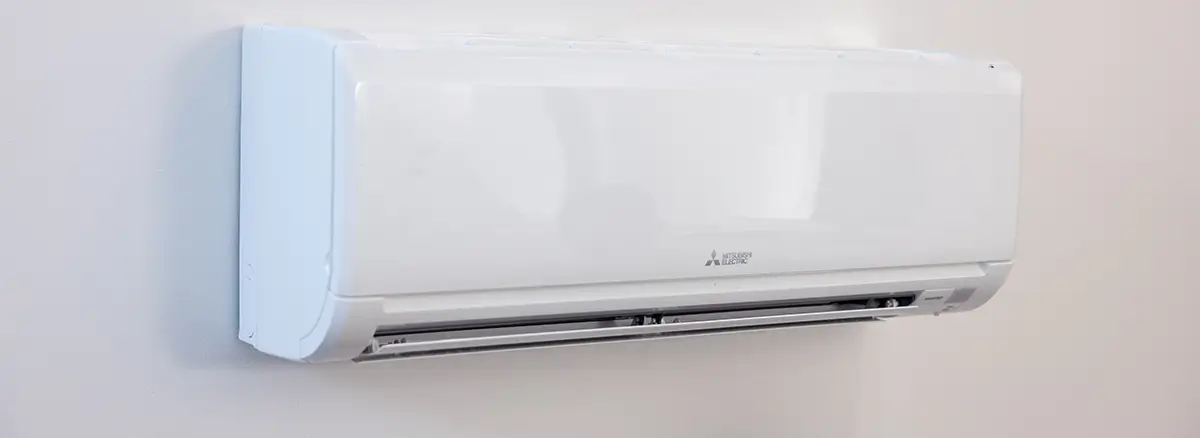
Ductless heating and cooling systems, also known as “heat pumps” or “mini-splits” are a clean…
Continue readingHow To Put An End To “Thermostat Wars” in Your Home
According to Mitsubishi, 71% of homeowners suffer from “thermostat wars” in their home. That’s…
Continue readingHarnessing Solar Heating
Solar heating systems have emerged as a popular and eco-conscious solution for homeowners looking to reduce their energy bills and environmental footprint. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of solar heating, exploring its various aspects and offering valuable tips to maximize savings and efficiency while staying warm and comfortable at home.
Table of Contents
What is Solar Heating?
Solar heating is a technology that leverages sunlight to generate heat for your home, with two primary types: passive and active systems. Passive solar heating relies on architectural design to capture and distribute warmth naturally, while active solar heating utilizes solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity for heating purposes. Understanding how these systems function is key to optimizing your solar heating setup.
Assessing Solar Potential
Before investing in solar heating, it’s crucial to assess your location’s solar potential. Consider factors such as the amount of sunlight your area receives, the orientation of your property, and your home’s heating energy needs. This evaluation will help you determine if solar heating is a practical and cost-effective choice for your situation.
Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design is all about making the most of available sunlight and thermal mass to heat your home naturally. Through strategic architectural choices, such as south-facing windows and thermal mass materials, you can maximize passive solar heating. We’ll also share tips on optimizing these features to ensure consistent warmth.
Active Solar Heating
Active solar heating harnesses the power of solar panels to generate electricity for heating. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used to power fans or pumps for heating air or water. We’ll explain how solar panels work in active solar heating and how to integrate them effectively into your existing heating system.

Solar Heating Installation
Professional installation is essential to ensure the efficiency and longevity of your solar heating system. We’ll discuss the importance of hiring experienced contractors, the costs associated with installation, and available incentives and tax credits that can offset these expenses.
Maximizing Solar Heating Efficiency
Keeping your solar heating system in top condition is vital for saving money and energy. Regular maintenance, cleaning of solar panels, and routine inspections are key practices to ensure your system operates at peak efficiency.
Combining Solar with Backup Heating
While solar heating is an excellent primary source of warmth, having a backup heating system in place is essential for cloudy days or high heating demands. Learn how to seamlessly integrate backup heating and ensure a smooth transition when needed.
Smart Controls and Monitoring
Smart thermostats and monitoring tools offer advanced ways to optimize your solar heating system. Explore the benefits of remote control, energy monitoring apps, and weather forecast integration for real-time adjustments that boost efficiency.
Cost Savings of Solar Heating
Discover how solar heating can significantly lower your energy bills, shorten the payback period, and increase the value of your home. We’ll also explore the financial incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, that can make solar heating even more cost-effective.
Environmental Impact
Reducing your carbon footprint and minimizing reliance on non-renewable energy sources are essential aspects of solar heating. We’ll delve into the environmental benefits, including decreased greenhouse gas emissions and a contribution to a more sustainable future.
Summary
Solar heating is a smart investment that combines financial savings with environmental responsibility. By following the tips and guidelines provided in this article, you can embark on a journey towards a more sustainable and cost-effective home heating system, all while enjoying the warmth and comfort of your solar-powered home.
Maximizing Efficiency in Fireplaces
Fireplaces, beloved for their inviting warmth and aesthetic appeal, often come with the challenge of inefficiency and elevated energy costs. This guide aims to address these issues, offering key strategies to enhance the efficiency of both wood-burning and gas fireplaces. Our goal is to help you enjoy the comfort and ambiance of your fireplace, while optimizing its cost-effectiveness and environmental friendliness. Here are some tips to save on fireplace heating costs and keep your home warm.
Table of Contents
Use Seasoned Firewood
Using seasoned firewood is crucial for optimizing the efficiency of wood-burning fireplaces. Seasoned wood, characterized by its low moisture content, ignites more readily and burns hotter with less smoke. To ensure a supply of quality firewood, it’s essential to store and season the wood properly in a dry, well-ventilated area. This fundamental step significantly improves the efficiency of your wood-burning fireplace.
Glass Doors
Installing glass doors on your fireplace offers numerous benefits for efficiency, regardless of whether it’s wood-burning or gas. Glass doors help contain the heat generated by the fire, preventing it from escaping up the chimney. They also act as a barrier against drafts and block smoke and embers from entering your living space. Properly maintained glass doors can significantly reduce heat loss and enhance safety.
Add Fireplace Inserts
Consider investing in a fireplace insert to improve efficiency further, especially for wood-burning fireplaces. Fireplace inserts are specialized heating units designed to fit into an existing fireplace. They come in various types, including wood-burning, gas, and pellet inserts. These inserts increase heat output and reduce heat loss, making your fireplace a more efficient source of warmth. Ensure proper installation and consult with a professional to choose the right type for your needs.
Gas Fireplace Efficiency
For gas fireplaces, efficiency can be enhanced by choosing high-efficiency models that burn gas more cleanly and effectively. Annual maintenance, including cleaning and inspecting gas fireplaces, ensures they operate at peak efficiency. Consider using a programmable thermostat to regulate the temperature and avoid overheating when the fireplace is not in use.

Consider Chimney Sealing
Preventing drafts and heat loss through the chimney is essential for maximizing fireplace efficiency, whether it’s wood-burning or gas. When the fireplace is not in use, seal the chimney to block cold air from entering and warm air from escaping. There are various methods for chimney sealing, including chimney dampers, chimney balloons, and chimney caps. Regular chimney inspections and maintenance are also crucial to address any issues that may affect efficiency.
Efficient Fireplace Practices
In addition to the mentioned tips, several practices can further enhance fireplace efficiency, regardless of the type. Properly arranging and lighting the fire, using dampers and air vents effectively, and ensuring the damper is closed when the fireplace is not in use all contribute to better heat retention and reduced energy waste.
Energy Savings and Environmental Impact
Optimizing your fireplace efficiency not only saves energy but also has environmental benefits, regardless of whether it’s wood-burning or gas. Using seasoned firewood and ensuring efficient combustion can reduce carbon emissions and minimize the environmental impact of your fireplace. By making your fireplace more efficient, you contribute to a greener and more sustainable home heating solution.
Summary
Transforming your fireplace, whether wood-burning or gas, into a cozy and cost-efficient heating source is achievable with the right strategies. By using seasoned firewood, installing glass doors, considering fireplace inserts (for wood-burning fireplaces), sealing the chimney, and practicing efficient fireplace use, you can enjoy the warmth and ambiance of your hearth while reducing heating costs and your environmental footprint. Make the most of this beloved home feature by implementing these tips for a comfortable and eco-friendly living space.
The Home is the Castle: Half of Americans Don’t Leave the House Every Day
Home is the most important place in our lives, and one we always aim to make as comfortable as possible. Whether it’s furnishing and decorating to our every whim, or investing in smart home technology to keep it as cool or warm as we please, home is everything.
In 2024, we surveyed over 1,000 Americans on how they spend their time at home to see which rooms they stay in, which rooms they don’t use, and how much time they really spend in their own homes.
Table of Contents
Americans Average 17 Days without Leaving Home at a Time
Over 1 in 3 Americans have increased both the amount of delivery restaurant food and the amount of delivery groceries they ordered since 2019; this number spikes even more for urban residents, with 49% ordering more delivery food and 45% ordering more delivery groceries.
How much time do Americans spend at home daily?
When surveyed, Americans estimated that they spend an average of 17 hours daily at home. This is an increase of 2 hours from 2019.
48% of Americans don’t leave their house every day.
- Urbanites: 44%
- Suburbanites: 48%
- Rural: 53%
Americans leave their homes an average of 4 times per week.
Nearly 1 in 4 Americans currently feel isolated in their homes. For some, this can result in ‘cabin fever,’ or a feeling of needing to get out of the house, even when it’s not possible. About half of Americans have experienced cabin fever.
American Social Habits In & Out of the Home
Overall, Americans only see their friends an average of three times per month. Urbanites are the most social, possibly due to population density and proximity, meeting 3.3 times per month, while rural Americans only see their friends about 2.6 times per month. Suburbanites are on par with the national average, at 3.1 times a month.
American social habits have certainly changed since the pandemic. While about 45% socialize roughly the same amount, 43.5% socialize less, while an extroverted 11.6% actually socialize more.
When asked whether they typically socialize at home or outside the home, respondents were split about 50-50. For those that did socialize more in the home, they named comfort as the main reason they do so. Other reasons are because they’re doing activities better suited for the home, like to save money by not going out, find it easier to plan, and find their anxiety is better when they’re not in public.
Most Used Rooms in the Home
Americans love the living room. When asked which single room they spend the most waking time in, 44% responded the living room, followed by the main or master bedroom (28%), the office (12%), and the remainder include the family room, kitchen, dining room, and other bedrooms.
The love of the bedroom is not to be underestimated: it’s no shock people love the bedroom even in waking hours- 16% say they engage in popular TikTok trend “bed rotting,” or laying in bed and consuming passive entertainment like scrolling on the phone, and this number increases to 40% for Gen Zers.
Do Americans Use Their Whole Home?
It turns out, Americans spend the most time in just a portion of their home. When asked, over 1 in 5 Americans said they don’t use their whole home, instead spending the vast majority of their time in just a portion of it. We asked respondents what their home’s square footage was as well as the square footage of the room they used the most, and it turns out that on average, Americans spend the most time in just 56% of their homes. Broken down by setting, suburbanites spend the most time in the smallest portion of their homes – just 17%. Urbanites spend the most time in about 21% of the home, while rural Americans spend the most time in 54% of their home.
How Working From Home Affects Americans
Especially since COVID-19, many office workers are able to work at least some of the time from their homes, if not fully remotely.
- 69% of Americans work from home at least part time
- 33% work from home full time
- Of those, 78% have a designated workspace
Just over 1 in 3 (36%) have a more variable style of working, utilizing multiple rooms in the house, rather than just one designated workspace. Top rooms to work from include the living room, main bedroom, office, kitchen, and dining room.
Many enjoy a combination including the living room and bedroom with an assortment of other rooms. With so many different options, why choose?
Ways to Reduce the Higher Costs of Being At Home
With all this time spent in the home showing no signs of going back to the norms of 2019, utility costs are staying higher as we spend more time at home, using appliances, water, and ensuring that home temperatures stay comfortable. Paired with higher energy costs, this can spell trouble for the average consumer.
Here are some ways to reduce costs, even while you spend more time in the home:
● Invest in a Heat Pump
○ Heat pumps are incredibly efficient devices designed to replace traditional HVAC systems. Rather than using electricity to heat or cool a space, they use electricity to move heat from one place to another. As such, they use a fraction of the energy a traditional HVAC system does. Not only that, but heat pump systems allow you to control individual temperatures by room, so you can keep little-used rooms less climate controlled and conserve your power.
● Close Doors and Windows in Little-Used Rooms
○ Shutting windows and drawing curtains is a great way to conserve temperatures in little-used rooms and save on power by relying on your home’s insulation. When you’re only concerned with a few rooms in your home, concentrating your airflow to just those spaces can be another way to reduce those pesky power bills.
● Unplug unused appliances
○ All those plugged-in items add up to a considerable difference in electric bills; unplugging appliances will prevent “phantom” drain on your power and ensure more energy efficiency.
● Replace air conditioner filters
○ If you do have air conditioning or an HVAC system, proper maintenance ensures the long term efficiency of each appliance and makes it easier to keep space temperatures regulated without straining the system.
● Harness the Environment by Using Solar Power and Rain Barrels
○ If you’re a homeowner, look into investing in solar power for your house- while not applicable to every climate, harnessing the sun’s power can offset bills and sometimes earn a tax credit. Not only that but installing rain barrels can keep landscaping costs lower and provide you with easy access to water that doesn’t run up your bill, particularly during gardening season.
Making the home the best- and most energy efficient – it can be has never been more important, and we’re here to help ensure that your home is always the perfect temperature.
Methodology & Fair Use
In January 2024, we surveyed 1,006 individuals ages 18-75 on their habits and preferences around time in and out of the home. The average age was 42, and respondents were 50% male and 50% female. 30% rent their homes, 60% own their homes, and 10% live with family or otherwise are not payment-burdened to live in their homes. Sixty-five percent live in a single family home, 21% live in an apartment, 5% a townhome, 4% a condo, 4% a mobile home, 1% live in a multifamily or unlisted home type.
Fair Use
When using this data and research, please attribute by linking to this study and citing RYCOR HVAC.
Regular Scheduled HVAC Maintenance Plans
Regular scheduled HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) maintenance plans are essential for optimizing the performance of your heating system and extending its lifespan. These plans involve routine inspections, cleaning, and adjustments to ensure that your heating system operates efficiently and reliably. In this section, we’ll delve into the importance of HVAC maintenance plans and provide examples of maintenance tasks.
Table of Contents
Preventative Maintenance
Minimizing Breakdowns: Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate into costly breakdowns.
Optimizing Efficiency: Well-maintained heating systems operate more efficiently, saving you money on heating bills.
Safety: Maintenance includes safety checks to ensure that your heating system is not a potential source of hazards like gas leaks or carbon monoxide leaks.
Examples of HVAC Maintenance Tasks
Changing Air Filters: Regularly changing or cleaning air filters ensures proper airflow and reduces strain on your heating system.
Cleaning and Inspecting Components: Cleaning and inspecting burners, heat exchangers, and other critical components prevent soot buildup and maintain efficient heat transfer.
Lubricating Moving Parts: Lubricating moving parts such as motors and fans reduces friction, which can lead to energy efficiency improvements and a longer system lifespan.
Checking Thermostat Calibration: Calibrating and testing thermostats ensures accurate temperature control.
Inspecting Ventilation: Ensuring that vents, flues, and ducts are unobstructed and in good condition prevents airflow restrictions.
Testing Safety Controls: Testing safety controls, including the limit switch and pilot safety system, guarantees safe operation.
Measuring System Performance: HVAC technicians often measure temperature differentials, system pressure, and combustion efficiency to assess performance.
Refrigerant Inspection: For heat pump systems, inspecting and maintaining the refrigerant levels is crucial for optimal performance.
Inspecting Electrical Connections: Loose or damaged electrical connections can cause heating system malfunctions; inspection and tightening are necessary.
Cleaning Coils and Heat Exchangers: Dust and dirt buildup on coils and heat exchangers can impede heat transfer; cleaning ensures efficiency.
Testing Ignition Systems: For gas-fired heating systems, testing ignition systems and adjusting for optimal combustion is essential.

Scheduled Maintenance Plans
Regularly Scheduled Visits: HVAC maintenance plans typically include scheduled visits by a professional technician at least once a year.
Priority Service: Many plans offer priority service in case of breakdowns or emergencies, reducing downtime and discomfort.
Discounts: Some maintenance plans include discounts on parts or repairs.
DIY vs. Professional Maintenance
Professional Expertise: While some maintenance tasks can be DIY, professional HVAC technicians have the expertise and tools to conduct thorough inspections and adjustments.
Comprehensive Service: Professional maintenance often includes a more comprehensive evaluation of your entire heating system.
Regular scheduled HVAC maintenance plans are an investment in the longevity and efficiency of your heating system. By addressing minor issues early and ensuring that your system is in peak condition, you can enjoy consistent warmth, lower energy bills, and fewer unexpected repairs over the life of your heating system.
Zone Heating
Zone heating is a smart approach to home heating that can significantly reduce your heating bill while enhancing comfort. It involves dividing your home into different heating zones, each with its thermostat and independent temperature control. This method allows you to heat only the areas that are in use, avoiding unnecessary heating expenses. In this section, we’ll explore what zone heating is and how it can help you save money, as well as the types of furnaces that support this energy-efficient strategy.
Table of Contents
What is Zone Heating?
Definition: Zone heating divides your home into distinct areas or zones, typically based on usage patterns or room layouts.
Individual Thermostats: Each zone is equipped with its thermostat, allowing for precise temperature control.
How Zone Heating Saves Money
Reduced Energy Consumption: By heating only the areas you occupy, zone heating minimizes energy wastage.
Customized Comfort: Family members can set temperatures according to their preferences, enhancing comfort.
Types of Furnaces that Support Zone Heating
Multi-Zone Systems: Some modern forced-air furnaces are designed to support multi-zone heating. These systems have multiple air handlers or dampers that can direct heat to different zones.
Ductless Mini-Split Systems: Ductless mini-split heat pumps are inherently suited for zone heating. Each indoor unit serves as a separate zone with its thermostat, offering efficient heating and cooling.
Hydronic Heating Systems: Radiant heating systems that use hot water or steam can be zoned with individual thermostats for different areas.

Benefits of Zone Heating
Energy Efficiency: Zone heating reduces the need to heat the entire house, leading to lower energy consumption and cost savings.
Enhanced Comfort: Different family members can enjoy customized comfort in their respective zones.
Reduced Wear and Tear: By not constantly running your heating system at full capacity, you can extend its lifespan and reduce maintenance costs.
Installation Considerations
Setting up a zone heating system often requires professional installation, including the installation of additional thermostats and zoning equipment. Properly planning and designing the zones is crucial to ensure efficient operation and desired comfort levels.
Zone heating offers a practical solution to optimizing your heating system’s efficiency and lowering your heating costs. By targeting the heating where it’s needed most and employing the appropriate type of furnace or heating system, you can enjoy the benefits of a more energy-efficient and cost-effective home heating strategy.
Top 50 Most Sustainable Small Cities in the U.S.
Climate change is increasingly affecting Americans nationwide; while there are many cities with entire departments devoted to climate consciousness and becoming more sustainable, what about the rest of America, and what makes a sustainable city?
We looked at over 100 small cities and towns and ranked them based on their number of EnergyStar buildings, walkability, farmer’s markets, and transit (both local and regional) to create a vision of America’s most sustainable cities and towns. Rather than look at initiatives or laws, focusing on infrastructure and built environment paves a blueprint for a more connected and climate-conscious future.
Table of Contents
America’s Most Sustainable Towns Study: 4 Key Takeaways
- America’s top 5 most sustainable towns: Bakersfield, CA; Lansing, MI; Wilmington, DE; Charlottesville, VA; and Grand Junction, CO
- The West and Midwest sport the most climate-conscious towns in the U.S.
- Most walkable cities: Butte, MT and Wilmington, DE
- Cities with the most farmers’ markets: Anchorage, AK and Duluth, MN
What are the Most Sustainable Small Cities in the U.S.?
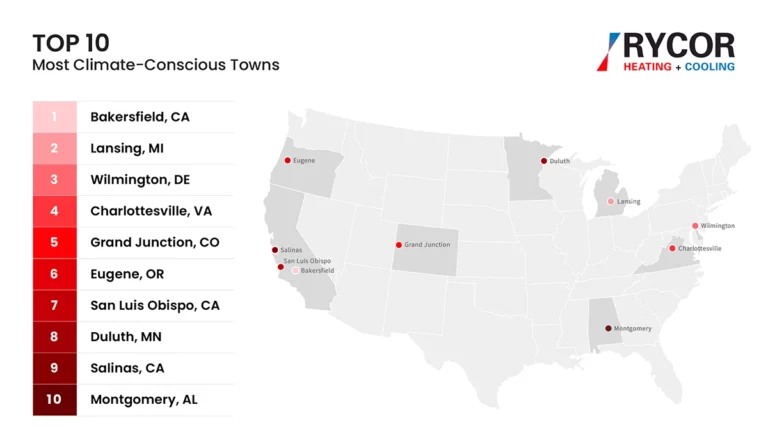
To determine climate consciousness, we focused on green infrastructure and different eco-friendly ways of addressing climate change. EnergyStar buildings are energy efficient and drain the grid less; farmer’s markets provide a climate-conscious approach to food systems; alternative fuel stations provide green alternatives to fossil fuels; walkability, public transit, and Amtrak stations all show a less car-reliant future on both the local and regional scale.
With all of these factors in mind, Bakersfield, CA, is the most climate-conscious and sustainable town in the U.S., followed by Lansing, MI and Wilmington, DE. Rounding out the top five are Charlottesville, VA and Grand Junction, CO.
To complete the top 10, Eugene, OR and San Luis Obispo, CA continue the strong West Coast presence, followed by Duluth, MN; Salinas, CA; and Montgomery, AL.
Full Ranking: America’s Most Sustainable & Climate-Conscious Towns
The full results of the ranking show that the West Coast is generally the most climate-conscious region of the U.S., with its higher number of both EnergyStar buildings and alternative fuel stations. Four of the top 10 cities for alternative fuel stations are in California alone!
The Best Towns for Farmers’ Markets, Walkability, and Alternative Fuel
Best Towns and Small Cities for Farmers Markets:
- Anchorage, AK
- Duluth, MN
- Lansing, MI
- Wilmington, DE
- Watertown, NY
We used the USDA’s Farmer’s Market Database to count the number of farmer’s markets listed in each town or small city in our rankings, and Anchorage, Alaska came out head and shoulders above the rest, with 14 markets. Duluth, Minnesota comes in second with 10, followed by Lansing, Michigan with 8 markets.
Best Towns for Alternative Fuel Stations:
- Bakersfield, CA
- San Luis Obispo, CA
- Eugene, OR
- Lansing, MI
- Santa Barbara, CA
Using the EPA’s database of alternative fuel stations, including everything from EV charging stations to biofuel and more, Bakersfield, California comes out as one of the greenest cities in the U.S. with 97 alternative fuel stations!
Most Walkable Small Cities in the US:
- Butte, MT
- Wilmington, DE
- Missoula, MT
- Salinas, CA
- Fargo, ND
What makes a city the most walkable? We used the EPA’s Walkability Index, which charts walkability to U.S. census tracts, and averaged each score to cover the area of each town or city.
One Way to Make Your Home More Eco-Friendly
Whether you’re looking to move or simply to understand how your town stacks up in terms of sustainability, each of these towns and small cities offers a greener vision of the future. But if you don’t live in these places, that doesn’t mean you can’t be greener!
One great step towards making your home more sustainable is installing a heat pump, or mini-split heating system. They only use the energy necessary to heat or cool a home, which makes them more climate conscious- and wallet conscious. Get in touch and see if you’re a good fit for a heat pump today!
Methodology & Fair Use
Sources:
- Farmers’ Market Database (USDA)
- Walkability Index (EPA) – to determine this score, census tracts within a given city or town were averaged to create the final score
- Alternative Fuel Stations (EPA)
- Amtrak Stations
- EnergyStar Buildings
- Public transit – modes were found by finding the department of transportation for each small city or town and reporting findings.
The full town list was determined by selecting every town named in the 100 smallest DMAs in the United States. Initial analysis looked at over 137 towns before selecting the top 50 in this ranking.
Each ranking factor was normalized on a ten point scale; modes of public transit were 10 points each, and Amtrak station presence accounted for either 0 points or 10 points. The final score out of 10 was determined by finding the average of all six categories.
Fair Use
When using this data and research, please attribute by linking to this study and citing RYCOR HVAC.










